Demographics of Cambodia
| Demographics of Cambodia | |
|---|---|
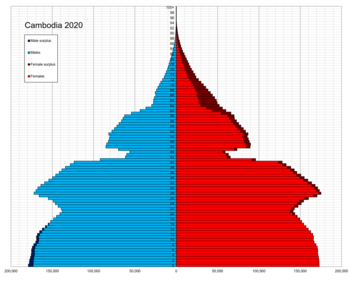 Cambodia population pyramid in 2020 | |
| Population | 16,946,438 |
| Growth rate | |
| Birth rate | 19.3 births/1,000 population (2021 est.)[1] |
| Death rate | 6.8 deaths/1,000 population (2021 est.) |
| Life expectancy | 69.6 years (2018 est.)[2] |
| • male | 67.3 years |
| • female | 71.6 years |
| Fertility rate | 2.34 children born/woman (2021 est.) |
| Infant mortality rate | 24 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)[3] |
| Net migration rate | |
| Age structure | |
| 0–14 years | 28.59% |
| 15–64 years | 65.26% |
| 65 and over | 6.15% |
| Sex ratio | |
| Total | 0.94 male(s)/female (2013) |
| At birth | 1.05 male(s)/female |
| 65 and over | 0.6 male(s)/female |
| Nationality | |
| Nationality | noun: Cambodian(s), Khmer(s); Kampuchean(s) (historical) adjective: Cambodian, Khmer; Kampuchean (historical) |
| Major ethnic | Khmer |
| Minor ethnic | Chinese, Vietnamese, Cham, and others |
| Language | |
| Official | Khmer |
Demographic features of the population of Cambodia include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
Population size and structure
[edit]| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1876 | 890,000 | — |
| 1901 | 1,103,000 | +0.86% |
| 1911 | 1,487,900 | +3.04% |
| 1921 | 2,402,600 | +4.91% |
| 1931 | 2,806,000 | +1.56% |
| 1947 | 3,296,000 | +1.01% |
| 1951 | 4,261,000 | +6.63% |
| 1961 | 5,510,000 | +2.60% |
| 1971 | 7,270,000 | +2.81% |
| 1981 | 6,682,000 | −0.84% |
| 1991 | 8,810,000 | +2.80% |
| 2001 | 12,353,000 | +3.44% |
| 2011 | 14,701,717 | +1.76% |
| 2021 | 16,946,438 | +1.43% |
| Source: CIA World Factbook | ||

Between 1874 and 1921, the total population of Cambodia increased from about 946,000 to 2.4 million. By 1950, it had increased to between 3,710,107 and 4,073,967, and in 1962 it had reached 5.7 million. From the 1960s until 1975, the population of Cambodia increased by about 2.2% yearly, the lowest increase in Southeast Asia.
By 1975 when the Khmer Rouge took power, the population was estimated at 7.3 million. Of this total an estimated one to two million reportedly died between 1975 and 1978. In 1981, the PRK gave the official population figure as nearly 6.7 million, although approximately 6.3 million to 6.4 million is probably more accurate.
The average annual rate of population growth from 1978 to 1985 was 2.3% (see table 2, Appendix A). A post-Khmer Rouge baby boom pushed the population above 10 million, although growth has slowed in recent years.
In 1959, about 45% of the population was under 15 years of age. By 1962, this had increased slightly to 46%. In 1962, an estimated 52% of the population was between 15 and 64 years of age, while 2% were older than 65. The percentage of males and females in the three groups was almost the same.
Age distribution
[edit]-
Cambodian Population Pyramid-2005
-
Population pyramid, urban-rural, Cambodia, 2019[4]
| Year[5] | Total population (thousands) | Population percentage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aged 0–14 | aged 15–64 | aged 65+ | ||
| 1950 | 4 346 | |||
| 1955 | 4 840 | |||
| 1960 | 5 433 | |||
| 1965 | 6 141 | |||
| 1970 | 6 938 | |||
| 1975 | 7 308 | |||
| 1980 | 6 306 | |||
| 1985 | 7 920 | |||
| 1990 | 9 532 | |||
| 1995 | 11 169 | |||
| 2000 | 12 447 | |||
| 2005 | 13 358 | |||
| 2010 | 14 138 | |||
| 2015 | 15 521 | |||
| 2020 | 16 719 | |||
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 7 320 112 | 7 642 479 | 14 962 591 | 100 |
| 0–4 | 806 531 | 777 854 | 1 584 385 | 10.59 |
| 5–9 | 721 480 | 693 339 | 1 414 819 | 9.46 |
| 10–14 | 768 899 | 735 963 | 1 504 862 | 10.06 |
| 15–19 | 878 612 | 830 980 | 1 709 592 | 11.43 |
| 20–24 | 848 931 | 800 737 | 1 649 668 | 11.03 |
| 25–29 | 678 825 | 712 044 | 1 390 869 | 9.30 |
| 30–34 | 613 674 | 637 973 | 1 251 647 | 8.37 |
| 35–39 | 338 735 | 363 397 | 702 132 | 4.69 |
| 40–44 | 411 072 | 441 415 | 852 487 | 5.70 |
| 45–49 | 344 372 | 395 214 | 739 586 | 4.94 |
| 50–54 | 295 645 | 352 214 | 648 347 | 4.33 |
| 55–59 | 190 528 | 288 806 | 479 334 | 3.20 |
| 60–64 | 153 721 | 218 867 | 372 588 | 2.49 |
| 65–69 | 105 605 | 147 502 | 253 107 | 1.69 |
| 70–74 | 76 017 | 108 069 | 184 086 | 1.23 |
| 75–79 | 47 601 | 72 558 | 120 159 | 0.80 |
| 80+ | 39 864 | 65 059 | 104 923 | 0.70 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
| 0–14 | 2 296 910 | 2 207 156 | 4 504 066 | 30.10 |
| 15–64 | 4 754 115 | 5 042 135 | 9 796 250 | 65.47 |
| 65+ | 269 087 | 393 188 | 662 275 | 4.43 |
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 8 093 453 | 8 498 636 | 16 592 089 | 100 |
| 0–4 | 791 593 | 755 468 | 1 547 061 | 9.32 |
| 5–9 | 792 080 | 756 481 | 1 548 561 | 9.33 |
| 10–14 | 843 604 | 804 317 | 1 647 921 | 9.93 |
| 15–19 | 799 876 | 773 934 | 1 573 810 | 9.49 |
| 20–24 | 647 446 | 666 588 | 1 314 034 | 7.92 |
| 25–29 | 684 545 | 720 947 | 1 405 492 | 8.47 |
| 30–34 | 682 783 | 713 536 | 1 396 319 | 8.42 |
| 35–39 | 684 224 | 703 803 | 1 388 027 | 8.37 |
| 40–44 | 483 437 | 500 719 | 984 156 | 5.93 |
| 45–49 | 369 988 | 393 527 | 763 515 | 4.60 |
| 50–54 | 360 130 | 409 250 | 769 380 | 4.64 |
| 55–59 | 319 093 | 370 486 | 689 579 | 4.16 |
| 60–64 | 232 929 | 310 156 | 543 085 | 3.27 |
| 65–69 | 157 661 | 240 966 | 398 627 | 2.40 |
| 70–74 | 112 069 | 169 150 | 281 219 | 1.69 |
| 75–79 | 71 156 | 105 568 | 176 724 | 1.07 |
| 80+ | 60 839 | 103 740 | 164 579 | 0.99 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
| 0–14 | 2 427 277 | 2 316 266 | 4 743 543 | 28.59 |
| 15–64 | 5 264 451 | 5 562 946 | 10 827 397 | 65.26 |
| 65+ | 401 725 | 619 424 | 1 021 149 | 6.15 |
Urbanization
[edit]- Urban population: 39.4% of total population (2019)[8]
- Rate of urbanization: 7.8% annual rate of change (2008—2019)
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Vital statistics
[edit]Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
UN estimates
[edit]| Period[9] | Population (on 1 July) |
Live births | Deaths | Natural change | CBR1 | CDR1 | NC1 | TFR1 | IMR1 | Life expectancy (years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 4 380 000 | 209 000 | 107 000 | 102 000 | 47.7 | 24.4 | 23.3 | 6.63 | 172.5 | 38.94 |
| 1951 | 4 485 000 | 213 000 | 108 000 | 105 000 | 47.5 | 24.1 | 23.4 | 6.62 | 170.9 | 39.25 |
| 1952 | 4 593 000 | 218 000 | 110 000 | 109 000 | 47.5 | 23.9 | 23.6 | 6.63 | 168.9 | 39.51 |
| 1953 | 4 702 000 | 224 000 | 112 000 | 112 000 | 47.6 | 23.7 | 23.9 | 6.66 | 167.5 | 39.74 |
| 1954 | 4 814 000 | 230 000 | 112 000 | 117 000 | 47.7 | 23.3 | 24.4 | 6.69 | 165.1 | 40.22 |
| 1955 | 4 931 000 | 236 000 | 114 000 | 122 000 | 47.8 | 23.1 | 24.7 | 6.73 | 163.4 | 40.45 |
| 1956 | 5 052 000 | 241 000 | 115 000 | 126 000 | 47.8 | 22.8 | 24.9 | 6.75 | 160.8 | 40.77 |
| 1957 | 5 176 000 | 247 000 | 116 000 | 130 000 | 47.6 | 22.5 | 25.1 | 6.75 | 158.2 | 41.19 |
| 1958 | 5 298 000 | 245 000 | 117 000 | 128 000 | 46.2 | 22.0 | 24.2 | 6.57 | 155.6 | 41.52 |
| 1959 | 5 419 000 | 244 000 | 117 000 | 127 000 | 45.0 | 21.6 | 23.3 | 6.42 | 152.5 | 41.79 |
| 1960 | 5 542 000 | 242 000 | 116 000 | 126 000 | 43.7 | 21.0 | 22.7 | 6.25 | 149.5 | 42.36 |
| 1961 | 5 665 000 | 242 000 | 116 000 | 127 000 | 42.8 | 20.4 | 22.3 | 6.12 | 147.0 | 42.79 |
| 1962 | 5 789 000 | 242 000 | 115 000 | 127 000 | 41.9 | 19.9 | 22.0 | 6.00 | 144.3 | 43.32 |
| 1963 | 5 914 000 | 242 000 | 114 000 | 128 000 | 40.9 | 19.3 | 21.6 | 5.85 | 141.7 | 43.90 |
| 1964 | 6 041 000 | 248 000 | 114 000 | 134 000 | 41.0 | 18.9 | 22.1 | 5.86 | 139.2 | 44.40 |
| 1965 | 6 171 000 | 252 000 | 115 000 | 137 000 | 40.8 | 18.5 | 22.2 | 5.82 | 136.9 | 44.79 |
| 1966 | 6 299 000 | 255 000 | 114 000 | 141 000 | 40.5 | 18.1 | 22.4 | 5.77 | 134.6 | 45.36 |
| 1967 | 6 426 000 | 258 000 | 115 000 | 143 000 | 40.1 | 17.9 | 22.2 | 5.71 | 132.3 | 45.51 |
| 1968 | 6 553 000 | 261 000 | 116 000 | 145 000 | 39.8 | 17.7 | 22.1 | 5.65 | 130.1 | 45.79 |
| 1969 | 6 680 000 | 263 000 | 116 000 | 147 000 | 39.4 | 17.4 | 22.0 | 5.56 | 128.0 | 46.24 |
| 1970 | 6 709 000 | 277 000 | 154 000 | 123 000 | 40.7 | 22.6 | 18.1 | 5.72 | 126.3 | 39.13 |
| 1971 | 6 696 000[clarification needed] | 276 000 | 150 000 | 125 000[clarification needed] | 40.9 | 22.3 | 18.6 | 5.87 | 124.7 | 39.51 |
| 1972 | 6 766 000 | 283 000 | 148 000 | 136 000 | 41.7 | 21.7 | 20.0 | 5.99 | 121.9 | 40.22 |
| 1973 | 6 852 000 | 269 000 | 150 000 | 119 000 | 39.2 | 21.8 | 17.4 | 5.56 | 125.0 | 40.02 |
| 1974 | 6 913 000 | 240 000 | 150 000 | 90 000 | 34.6 | 21.6 | 13.0 | 4.80 | 126.9 | 39.80 |
| 1975 | 6 728 000 | 210 000 | 578 000 | −368 000 | 31.2 | 85.7 | −54.6 | 4.10 | 265.4 | 12.00 |
| 1976 | 6 307 000 | 175 000 | 548 000 | −373 000 | 27.6 | 86.6 | −58.9 | 3.41 | 173.1 | 12.01 |
| 1977 | 6 040 000 | 140 000 | 192 000 | −52 000 | 23.1 | 31.7 | −8.7 | 2.72 | 134.2 | 28.91 |
| 1978 | 5 961 000 | 171 000 | 136 000 | 35 000 | 28.4 | 22.6 | 5.8 | 3.34 | 131.2 | 36.98 |
| 1979 | 6 052 000 | 227 000 | 114 000 | 113 000 | 37.9 | 19.1 | 18.8 | 4.56 | 117.9 | 42.28 |
| 1980 | 6 199 000 | 301 000 | 104 000 | 198 000 | 48.0 | 16.5 | 31.5 | 5.77 | 115.8 | 47.57 |
| 1981 | 6 364 000 | 311 000 | 106 000 | 205 000 | 49.1 | 16.7 | 32.4 | 6.04 | 112.8 | 48.18 |
| 1982 | 6 620 000 | 333 000 | 109 000 | 224 000 | 50.3 | 16.5 | 33.9 | 6.19 | 109.4 | 48.74 |
| 1983 | 6 882 000 | 350 000 | 111 000 | 239 000 | 51.0 | 16.1 | 34.8 | 6.30 | 106.1 | 49.49 |
| 1984 | 7 134 000 | 367 000 | 113 000 | 254 000 | 51.3 | 15.7 | 35.6 | 6.34 | 102.7 | 50.24 |
| 1985 | 7 376 000 | 374 000 | 113 000 | 261 000 | 50.6 | 15.3 | 35.4 | 6.31 | 99.6 | 51.04 |
| 1986 | 7 661 000 | 380 000 | 114 000 | 266 000 | 49.7 | 14.9 | 34.8 | 6.23 | 96.7 | 51.51 |
| 1987 | 7 976 000 | 387 000 | 109 000 | 278 000 | 48.7 | 13.7 | 35.0 | 6.10 | 94.1 | 53.45 |
| 1988 | 8 270 000 | 393 000 | 109 000 | 284 000 | 47.5 | 13.2 | 34.3 | 5.94 | 91.2 | 54.28 |
| 1989 | 8 571 000 | 390 000 | 109 000 | 281 000 | 45.6 | 12.7 | 32.9 | 5.72 | 88.6 | 54.80 |
| 1990 | 8 911 000 | 398 000 | 109 000 | 289 000 | 44.8 | 12.2 | 32.5 | 5.64 | 86.2 | 55.43 |
| 1991 | 9 259 000 | 404 000 | 111 000 | 294 000 | 43.8 | 12.0 | 31.8 | 5.57 | 86.4 | 55.79 |
| 1992 | 9 718 000 | 406 000 | 113 000 | 294 000 | 42.4 | 11.8 | 30.6 | 5.45 | 86.4 | 56.02 |
| 1993 | 10 244 000 | 414 000 | 117 000 | 297 000 | 40.8 | 11.5 | 29.3 | 5.27 | 87.0 | 56.08 |
| 1994 | 10 636 000 | 411 000 | 121 000 | 290 000 | 38.6 | 11.4 | 27.3 | 5.05 | 88.3 | 56.04 |
| 1995 | 10 920 000 | 395 000 | 121 000 | 274 000 | 36.2 | 11.1 | 25.1 | 4.82 | 88.6 | 56.31 |
| 1996 | 11 183 000 | 377 000 | 121 000 | 256 000 | 33.7 | 10.8 | 22.9 | 4.59 | 89.0 | 56.35 |
| 1997 | 11 432 000 | 362 000 | 120 000 | 242 000 | 31.7 | 10.5 | 21.2 | 4.39 | 88.5 | 56.74 |
| 1998 | 11 669 000 | 343 000 | 118 000 | 225 000 | 29.4 | 10.2 | 19.3 | 4.14 | 87.2 | 57.03 |
| 1999 | 11 899 000 | 341 000 | 116 000 | 225 000 | 28.7 | 9.7 | 18.9 | 3.92 | 84.4 | 57.69 |
| 2000 | 12 119 000 | 334 000 | 112 000 | 222 000 | 27.6 | 9.3 | 18.3 | 3.77 | 79.9 | 58.63 |
| 2001 | 12 338 000 | 332 000 | 107 000 | 225 000 | 26.9 | 8.7 | 18.3 | 3.65 | 73.2 | 59.97 |
| 2002 | 12 562 000 | 332 000 | 102 000 | 230 000 | 26.4 | 8.1 | 18.3 | 3.56 | 66.4 | 61.23 |
| 2003 | 12 788 000 | 331 000 | 98 000 | 233 000 | 25.9 | 7.6 | 18.2 | 3.44 | 60.4 | 62.52 |
| 2004 | 13 016 000 | 332 000 | 95 000 | 237 000 | 25.5 | 7.3 | 18.2 | 3.35 | 55.3 | 63.55 |
| 2005 | 13 247 000 | 334 000 | 93 000 | 241 000 | 25.2 | 7.0 | 18.1 | 3.24 | 51.0 | 64.29 |
| 2006 | 13 478 000 | 336 000 | 92 000 | 244 000 | 24.9 | 6.8 | 18.1 | 3.15 | 47.4 | 65.06 |
| 2007 | 13 715 000 | 342 000 | 91 000 | 251 000 | 24.9 | 6.6 | 18.3 | 3.08 | 44.3 | 65.73 |
| 2008 | 13 944 000 | 341 000 | 90 000 | 252 000 | 24.5 | 6.4 | 18.0 | 2.97 | 41.3 | 66.47 |
| 2009 | 14 156 000 | 342 000 | 87 000 | 255 000 | 24.1 | 6.1 | 18.0 | 2.87 | 38.4 | 67.44 |
| 2010 | 14 364 000 | 340 000 | 88 000 | 252 000 | 23.7 | 6.1 | 17.5 | 2.77 | 35.7 | 67.71 |
| 2011 | 14 574 000 | 341 000 | 87 000 | 254 000 | 23.4 | 5.9 | 17.4 | 2.70 | 33.4 | 68.42 |
| 2012 | 14 787 000 | 345 000 | 87 000 | 258 000 | 23.3 | 5.9 | 17.4 | 2.66 | 31.0 | 68.92 |
| 2013 | 15 000 000 | 346 000 | 87 000 | 259 000 | 23.0 | 5.8 | 17.2 | 2.62 | 29.3 | 69.30 |
| 2014 | 15 211 000 | 347 000 | 88 000 | 259 000 | 22.8 | 5.8 | 17.0 | 2.59 | 27.8 | 69.74 |
| 2015 | 15 418 000 | 345 000 | 90 000 | 255 000 | 22.3 | 5.8 | 16.5 | 2.55 | 26.4 | 69.87 |
| 2016 | 15 625 000 | 342 000 | 90 000 | 252 000 | 21.9 | 5.8 | 16.1 | 2.51 | 25.3 | 70.22 |
| 2017 | 15 831 000 | 338 000 | 92 000 | 247 000 | 21.3 | 5.8 | 15.6 | 2.47 | 24.2 | 70.52 |
| 2018 | 16 025 000 | 334 000 | 94 000 | 240 000 | 20.8 | 5.9 | 14.9 | 2.44 | 23.3 | 70.56 |
| 2019 | 16 208 000 | 329 000 | 97 000 | 233 000 | 20.3 | 5.9 | 14.3 | 2.40 | 22.4 | 70.69 |
| 2020 | 16 397 000 | 326 000 | 102 000 | 223 000 | 19.8 | 6.2 | 13.6 | 2.38 | 21.6 | 70.42 |
| 2021 | 16 589 000 | 321 000 | 114 000 | 207 000 | 19.3 | 6.8 | 12.5 | 2.34 | 20.8 | 69.58 |
| 1 CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); CDR = crude death rate (per 1000); NC = natural change (per 1000); TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman); IMR = infant mortality rate per 1000 births | ||||||||||
Fertility
[edit]The total fertility rate in Cambodia was 3.0 children per woman in 2010.[10] The fertility rate was 4.0 children in 2000.[10] Women in urban areas have 2.2 children on average, compared with 3.3 children per woman in rural areas.[10] Fertility is highest in Mondol Kiri and Rattanak Kiri Provinces, where women have an average of 4.5 children, and lowest in Phnom Penh where women have an average of 2.0 children.[10]
Demographic and Health Surveys
[edit]Total Fertility Rate (TFR) (Wanted Fertility Rate) and Crude Birth Rate (CBR):[11] [12][13]
| Year | Total | Urban | Rural | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBR | TFR | CBR | TFR | CBR | TFR | |
| 1995–1998 | 29.0 | 4.11 | 25.0 | 3.31 | 29.0 | 4.25 |
| 2000 | 27.7 | 4.0 (3.1) | 23.9 | 3.1 (2.5) | 28.3 | 4.2 (3.2) |
| 2005 | 25.6 | 3.4 (2.8) | 23.8 | 2.8 (2.3) | 25.9 | 3.5 (2.9) |
| 2010 | 24.2 | 3.0 (2.6) | 21.0 | 2.2 (2.0) | 25.0 | 3.3 (2.8) |
| 2014 | 22.0 | 2.7 (2.4) | 20.2 | 2.1 (1.9) | 22.4 | 2.9 (2.6) |
| 2021–22 | 20.2 | 2.7 (2.4) | 20.5 | 2.4 (2.2) | 20.1 | 3.0 (2.7) |

Total fertility rate and other related statistics by province, as of 2014:[14]
| Province | Total fertility rate | Percentage of women age 15-49 currently pregnant | Completed fertility rate (Average number of children born per woman in her lifetime) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Banteay Meanchey | 2.8 | 5.2 | 4.0 |
| Kampong Cham | 3.3 | 3.5 | 3.9 |
| Kampong Chhnang | 2.4 | 5.4 | 4.2 |
| Kampong Speu | 2.4 | 6.3 | 4.1 |
| Kampong Thom | 2.9 | 5.8 | 4.4 |
| Kandal | 2.5 | 5.7 | 3.9 |
| Kratié | 3.6 | 7.3 | 4.5 |
| Phnom Penh | 2.0 | 4.6 | 2.8 |
| Prey Veng | 3.0 | 4.9 | 3.5 |
| Pursat | 3.1 | 5.9 | 4.0 |
| Siem Reap | 2.7 | 5.2 | 3.9 |
| Svay Rieng | 2.5 | 5.7 | 3.4 |
| Takéo | 2.4 | 3.9 | 3.7 |
| Oddar Meanchey | 3.0 | 8.5 | 4.6 |
| Battambang/Pailin | 2.9 | 5.5 | 3.8 |
| Kampot/Kep | 2.5 | 4.9 | 3.9 |
| Sihanoukville/Koh Kong | 2.7 | 5.8 | 4.1 |
| Preah Vihear/Stung Treng | 3.6 | 9.5 | 5.2 |
| Mondulkiri/Ratanakiri | 3.3 | 6.9 | 4.8 |
Infant and childhood mortality
[edit]Childhood mortality rates are decreasing in Cambodia.[10] Currently, the infant mortality rate is 45 deaths per 1,000 live births for the five-year period before the survey compared with 66 deaths reported in the 2005 CDHS and 95 in the 2000 CDHS. Under-five mortality rates have also decreased from 124 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2000, 83 deaths in 2005 to 54 deaths per 1,000 in 2010.
Childhood mortality decreases markedly with mother's education and wealth. Infant mortality, for example, is twice as high among children whose mothers have no schooling compared to those with secondary or higher education (72 versus 31). The association with wealth is even stronger. There are 77 deaths per 1,000 live births among infants from the poorest households compared to only 23 deaths per 1,000 live births among infants from the richest households.
Mortality rates are much higher in rural than urban areas. Infant mortality, for example, is 64 deaths per 1,000 live births in rural areas compared to only 22 in urban areas. Mortality also differs by province. Infant mortality ranges from only 13 deaths per 1,000 live births in Phnom Penh to 78 deaths per 1,000 live births in Kampong Chhnang and Svay Rieng.
Life expectancy
[edit]
In 1959, life expectancy at birth was 44.2 years for males and 43.3 years for females. By 1970, life expectancy had increased by about 2.5 years since 1945. The greater longevity for females apparently reflected improved health practices during maternity and childbirth.
| Period | Life expectancy in Years |
Period | Life expectancy in Years |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 40.3 | 1985–1990 | 52.0 |
| 1955–1960 | 41.1 | 1990–1995 | 54.3 |
| 1960–1965 | 41.4 | 1995–2000 | 56.4 |
| 1965–1970 | 42.0 | 2000–2005 | 60.8 |
| 1970–1975 | 37.8 | 2005–2010 | 65.1 |
| 1975–1980 | 14.5 | 2010–2015 | 67.6 |
| 1980–1985 | 52.0 |
Source: UN World Population Prospects[15]
Ethnic groups
[edit]
The largest of the ethnic groups in Cambodia are the Khmer, who comprise 95.8% of the total population[4] in 2019 and primarily inhabit the lowland Mekong sub region and the central plains.
The Khmer historically have lived near the lower Mekong River in a contiguous arc that runs from the southern Khorat Plateau where modern-day Thailand, Laos and Cambodia meet in the northeast, stretching southwest through the lands surrounding Tonle Sap lake to the Cardamom Mountains, then continues back southeast to the mouth of the Mekong River in southeastern Vietnam.
Ethnic groups in Cambodia other than the politically and socially dominant Khmer are classified as either "indigenous ethnic minorities" or "non-indigenous ethnic minorities". The indigenous ethnic minorities, more commonly collectively referred to as the Khmer Loeu ("upland Khmer"), constitute the majority in the remote mountainous provinces of Ratanakiri, Mondulkiri and Stung Treng and are present in substantial numbers in Kratie Province.
Approximately 17-21 separate ethnic groups, most of whom speak Austroasiatic languages related to Khmer, are included in the Khmer Loeu designation, including the Kuy and Tampuan people. These peoples are considered by the Khmer to be the aboriginal inhabitants of the land. Two of these highland groups, the Rade and the Jarai, are Chamic peoples who speak Austronesian languages descended from ancient Cham. These indigenous ethnic minorities haven't integrated into Khmer culture and follow their traditional animist beliefs.
| Ethnic group |
Census 1998 | Census 2008 | Census 2019 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Khmer | 10,942,066 | 96.7 | 12,901,447 | 96.3 | 14,893,134 | 95.8 |
| Indigenous ethnic minorities | 276,081 | 2.4 | 383,273 | 2.9 | 448,282 | 2.9 |
| Cham | 179,193 | 1.52 | 272,217 | 1.77 | ||
| Bunong | 37,507 | 0.28 | 36,585 | 0.24 | ||
| Tampuan | 31,013 | 0.23 | 36,373 | 0.23 | ||
| Kuy | 28,612 | 0.21 | 16,762 | 0.11 | ||
| Jarai | 26,335 | 0.20 | 26,922 | 0.17 | ||
| Kreung | 19,988 | 0.15 | 21,453 | 0.14 | ||
| Brao | 9,025 | 0.07 | 10,086 | 0.06 | ||
| Stieng | 6,541 | 0.05 | 4,908 | 0.03 | ||
| Kavet | 6,218 | 0.05 | 7,569 | 0.05 | ||
| Kraol | 4,202 | 0.03 | 5,630 | 0.04 | ||
| Pear | 1,827 | 0.01 | 944 | 0.01 | ||
| Ro Ong | 1,831 | 0.01 | 573 | 0.00 | ||
| Mel | 1,697 | 0.01 | 984 | 0.01 | ||
| Thmoon | 865 | 0.01 | 1,164 | 0.01 | ||
| Suoy | 857 | 0.01 | 775 | 0.00 | ||
| Khogn | 743 | 0.01 | 109 | 0.00 | ||
| Klueng | 702 | 0.00 | 413 | 0.00 | ||
| Kchruk | 408 | 0.00 | 266 | 0.00 | ||
| Sa'och | 445 | 0.00 | 209 | 0.00 | ||
| Ta Mun | 400 | 0.00 | ||||
| Lon | 327 | 0.00 | 1,033 | 0.01 | ||
| K'nuh | 56 | 0.00 | ||||
| Mon | 19 | 0.00 | 27 | 0.00 | ||
| Rade | 21 | 0.00 | 179 | 0.00 | ||
| Kchak | 10 | 0.00 | 16 | 0.00 | ||
| K'jah | 5 | 0.00 | ||||
| Chinese | 26,721 | 0.2 | 6,530 | 0.05 | 94,450 | 0.6 |
| Vietnamese | 140,328 | 1.2 | 72,775 | 0.5 | 78,090 | 0.5 |
| Lao | 28,854 | 0.2 | 18,515 | 0.1 | 13,636 | 0.1 |
| Thai | 2,482 | 0.02 | 2,458 | 0.02 | 6,650 | 0.04 |
| Other | 25,124 | 0.2 | 10,684 | 0.1 | 17,769 | 0.1 |
| Total | 11,437,656 | 13,395,682 | 15,552,211 | |||
The non-indigenous ethnic minorities include immigrants and their descendants who live among the Khmer and have adopted, at least nominally, Khmer culture and language. The three groups most often included are the Chinese Cambodians, Vietnamese and Cham peoples. The Chinese have immigrated to Cambodia from different regions of China throughout Cambodia's history, integrating into Cambodian society and today Chinese Cambodians or Cambodians of mixed Sino-Khmer ancestry dominate the business community, politics and the media. The Cham are descendants of refugees from the various wars of the historical kingdom of Champa. The Cham live amongst the Khmer in the central plains but in contrast to the Khmer who are Theravada Buddhists, the vast majority of Cham follow Islam.[16]
There are also small numbers of other minority groups. Tai peoples in Cambodia include the Lao along the Mekong at the northeast border, Thai (urban and rural), and the culturally Burmese Kola, who have visibly influenced the culture of Pailin Province. Even smaller numbers of recent Hmong immigrants reside along the Lao border and various Burmese peoples have immigrated to the capital, Phnom Penh.
Languages
[edit]| Languages of Cambodia | |
|---|---|
 Poster in Khmer, 1954 | |
| Official | Khmer |
| Main | Khmer |
| Minority | |
| Foreign | |
| Signed | Cambodian Sign Language |
| Keyboard layout | |
- Official language
Khmer is an Austroasiatic language spoken by over 90% of the Cambodian population.[17] The vast majority of Khmer speakers use the Central Khmer dialect. Central Khmer is the variety spoken in the central plain where the ethnic Khmers most heavily concentrate. Other Khmer dialects include the Phnom Penh variety, as well as Northern Khmer (Surin Khmer), Western Khmer (Cardamom Khmer), Southern Khmer (Khmer Krom), and the Khmer Khe dialect in Stung Treng province.
The Northern Khmer dialect is also spoken by over a million Khmers in the southern regions of Northeast Thailand. Western Khmer displays features of the Middle Khmer language, and is considered a conservative dialect. Southern Khmer is the first language of the Khmer Krom people in the Mekong Delta region in Vietnam.
- Minority languages
According to Glottolog, 22 languages other than Khmer are spoken in Cambodia,[18] most of which are also Austroasiatic languages. Other Austroasiatic languages of Cambodia include Kuy, Por (Pear), Somray, Chong, Suoy, Sa'och, Tampuan, Kaco', Stieng, Mnong, Brao, Krung (Rade), and Sou (Laven).
Many of these languages are also spoken in Vietnam. Vietnamese itself is also spoken in parts of Cambodia.[19] Non-Austroasiatic minority languages of Cambodia include Cham, Jarai, and Mekong Delta Malay (Austronesian) as well as Thai and Lao (Tai-Kadai).
- Languages of education
English and French are used to different extents in education.[20][21]
- Sign language
- Cambodian Sign Language
Religions
[edit]- Buddhism: 97.1%, Islam: 2.0%, Christianity: 0.3%, Others: 0.5%
Emigration
[edit]Countries with notable populations of Cambodians are:
 Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam United States
United States France
France Malaysia
Malaysia Australia
Australia Canada
Canada New Zealand
New Zealand China
China
 UK
UK Laos
Laos Singapore
Singapore Switzerland
Switzerland South Korea
South Korea Japan
Japan
References
[edit]- ^ "Birth rate, crude (per 1,000 people) – Cambodia". World Bank. 8 June 2020.
- ^ "Life expectancy at birth, total (years) – Cambodia". World Bank. Retrieved 7 June 2020.
- ^ "Mortality rate, infant (per 1,000 live births) – Cambodia". World Bank. 7 June 2020.
- ^ a b c "General Population Census of Cambodia 2019" (PDF). National Institute of Statistics, Cambodia, p. 33.
- ^ "Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat, World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision".
- ^ "United Nations Statistics Division – Demographic and Social Statistics". Archived from the original on 21 September 2004.
- ^ "International Travel and Migration Statistics". UNSD. Retrieved 18 February 2023.
- ^ "General Population Census 2019 of the Kingdom of Cambodia" (PDF). National Institute of Statistics. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- ^ "World Population Prospects – Population Division – United Nations". population.un.org. Retrieved 13 July 2022.
- ^ a b c d e "National Institute of Statistics CAMBODIA DEMOGRAPHIC AND HEALTH SURVEY 2010".
- ^ "Cambodia – Demographic and Health Survey 2010".
- ^ "National Health Survey 1998" (PDF). DHS Program. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 March 2022. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- ^ "Cambodia demographic and health survey 2021-22" (Research report). DHS Program. June 2022. Retrieved 18 February 2023.
- ^ "Cambodia DHS, 2014 – Final Report (English)" (PDF).
- ^ "World Population Prospects – Population Division – United Nations". Retrieved 15 July 2017.
- ^ "Cambodia Ethnic Groups". Cambodia-travel.com. Archived from the original on 3 October 2018. Retrieved 2 September 2012.
- ^ Haiman, John. (2011). Cambodian : Khmer. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Pub. Co. ISBN 978-90-272-8502-7. OCLC 758491354.
- ^ "Glottolog 4.3 – Languages". glottolog.org. Retrieved 29 January 2021.
- ^ "Mother Tongue". Cambodia – Cambodia Inter-Censal Population Survey 2013, Count People and Households. Cambodian National Institute of Statistics. Archived from the original on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2017.
Warning: these figures indicate the number of cases found in the data file. They cannot be interpreted as summary statistics of the population of interest.
- ^ "The World Factbook". 13 December 2022.
- ^ (in French) La langue française dans le monde, 2014, Éditions Nathan, p. 18.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook (2025 ed.). CIA. (Archived 2008 edition.)
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook (2025 ed.). CIA. (Archived 2008 edition.)


![Population pyramid, urban-rural, Cambodia, 2019[4]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/a4/Population_pyramid_cambodia_2019.png/176px-Population_pyramid_cambodia_2019.png)



